Hearing loss affects millions of individuals across the globe, significantly influencing their quality of life and communication capabilities. To address hearing concerns effectively, it’s crucial to understand the underlying causes and types of hearing loss. This comprehensive guide will delve into the various factors contributing to hearing impairment, ensuring you are well-informed. We’ll also explore relevant audiology practices and the importance of hearing care in maintaining auditory health.
What is Hearing Loss?
Hearing loss refers to a partial or total inability to hear sounds in one or both ears. It can manifest in various degrees, from mild to profound. The prevalence of hearing loss has been on the rise owing to factors ranging from aging to prolonged exposure to loud noises.
Causes of Hearing Loss
The causes of hearing loss can be broadly classified into two categories: conductive and sensorineural. Understanding these categories can help in identifying the right audiology treatments and hearing aids.
Conductive Hearing Loss
Conductive hearing loss occurs when sound waves cannot efficiently travel through the ear canal to the eardrum and the tiny bones of the middle ear. The causes may include:
- Earwax Buildup: Excessive earwax can block the ear canal, preventing sound from reaching the eardrum.
- Fluid in the Ear: This is often due to infections, which can lead to temporary hearing loss.
- Perforated Eardrum: Injury or infections can create a hole in the eardrum, affecting hearing.
- Otosclerosis: A condition that affects the small bones in the ear, leading to conductive hearing loss.
Fortunately, many cases of conductive hearing loss can be treated with various interventions such as earwax removal, surgical procedures, or the use of hearing aids.
Sensorineural Hearing Loss
Sensorineural hearing loss results from damage to the inner ear or the auditory nerve pathways. This type of hearing loss is often permanent and includes factors such as:
- Age-Related Hearing Loss: As we age, the delicate structures of the ear can deteriorate, leading to gradual hearing impairment.
- Noise-Induced Hearing Loss: Prolonged exposure to loud sounds can irreversibly damage the hair cells in the cochlea.
- Genetic Factors: Some individuals may inherit conditions that affect their ability to hear.
- Illness: Certain illnesses, such as meningitis or Meniere's disease, can result in sensorineural hearing loss.
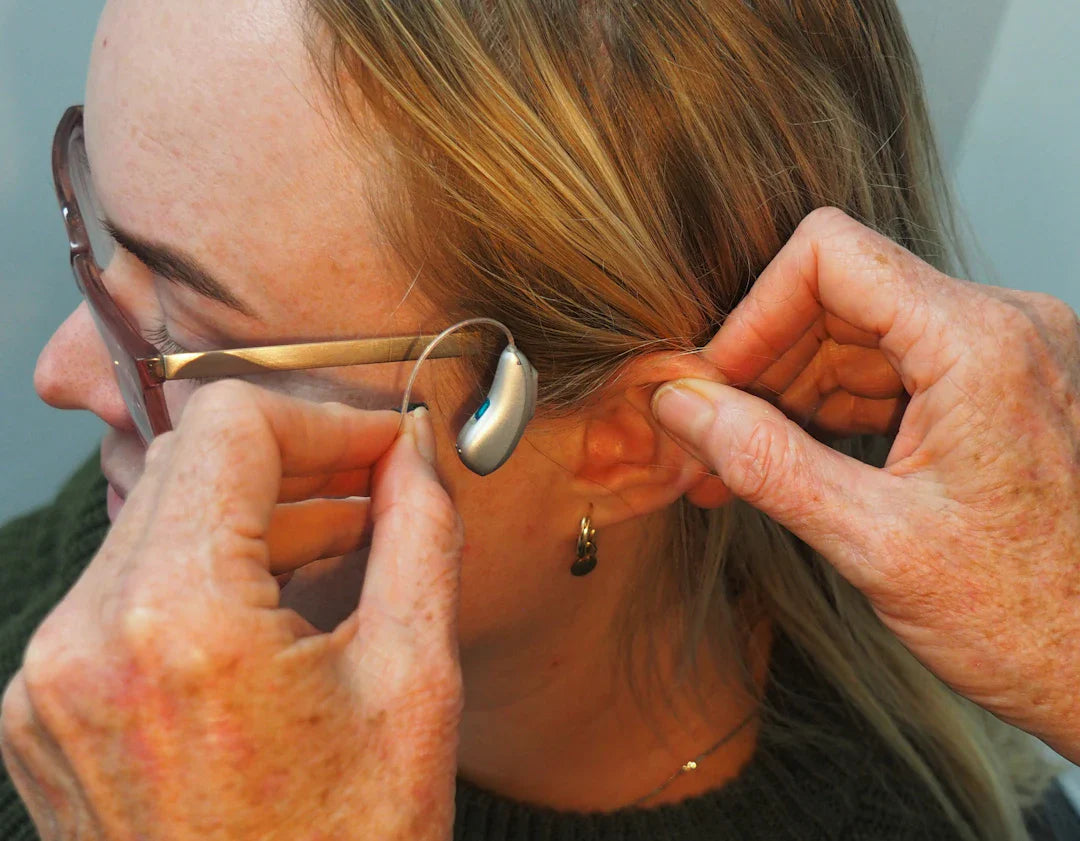
This type of hearing loss often requires ongoing audiology treatment and may be managed with hearing aids such as the GN Resound Nexia microRIE 5.
Types of Hearing Loss
Hearing loss can also be classified based on its severity:
Mild Hearing Loss
People with mild hearing loss can hear some speech sounds but may struggle to understand conversations, especially in noisy environments. They often benefit from hearing aids and audiology intervention.
Moderate Hearing Loss
Individuals with moderate hearing loss have a more significant challenge understanding speech without amplification. Hearing aids are often essential for improving communication abilities.
Severe Hearing Loss
Severe hearing loss makes it difficult to hear even loud sounds, and conversations are typically challenging, even with aids. Comprehensive hearing care and additional hearing devices may be necessary.
Profound Hearing Loss
This category represents the most serious level of hearing loss, where individuals may not hear even the loudest sounds. Options for communication can include sign language, cochlear implants, or advanced hearing aids.
Diagnosing Hearing Loss
Understanding your hearing capability is essential. If you suspect that you or a loved one may be experiencing hearing issues, it’s advisable to seek professional help. An audiologist can conduct various tests to determine the degree and type of hearing loss. Common assessment methods include:
- Pure-Tone Audiometry: This test measures the softest sounds a person can hear at different pitches.
- Tympanometry: Evaluates the condition of the middle ear and the mobility of the eardrum.
- Speech Audiometry: Assesses the ability to understand speech at varying volumes.
The Role of Audiology in Hearing Care
Audiology is a vital field that focuses on diagnosing, treating, and managing hearing loss. Audiologists offer personalized treatment plans tailored to individual needs, which may involve hearing aids, counselling, and auditory training. They play a crucial role in guiding patients through their hearing care journey, ensuring they maintain optimal auditory health.
Managing Hearing Loss with Hearing Aids
Hearing aids are essential tools for those experiencing hearing loss. They amplify sound, making it easier for users to engage in conversations and enjoy their favourite activities. The GN Resound Nexia microRIE 5 is an example of a widely recognised model, renowned for its exceptional performance and discreet design.
When considering hearing aids, it's essential to consult with an audiologist. They will help determine the most suitable device based on the degree of hearing loss, lifestyle preferences, and specific auditory needs.
The Importance of Regular Hearing Care
Just as regular check-ups are crucial for your overall health, consistently monitoring and caring for your hearing is equally important. Regular audiology appointments can help detect changes in hearing before they become severe, thus allowing for timely intervention and management.
Moreover, audiologists may also provide essential services such as earwax removal to maintain cleanliness and prevent hearing issues. Understanding your hearing health can empower you to make informed decisions about your lifestyle and communication.
Your Audiology Journey: What to Expect
When you visit an audiologist, you can expect a thorough evaluation tailored to your needs. The general process includes:
- Initial Consultation: Discuss your symptoms, medical history, and any concerns regarding your hearing.
- Hearing Tests: Undergo various assessments to determine the nature and extent of any hearing loss.
- Recommendations: Based on the results, the audiologist will advise on the best course of action, whether it involves hearing aids, lifestyle adjustments, or other therapies.
- Follow-Up: Regular follow-up appointments can help monitor your hearing and adjust treatments as needed.
Living Well with Hearing Loss
Adjusting to life with hearing loss can be challenging, but embracing effective communication and appropriate hearing aids can dramatically improve your experience. Here are a few tips to help manage your hearing loss effectively:
- Stay Engaged: Communicate openly with family and friends about your needs and preferences.
- Utilise Technology: Explore assistive listening devices and apps designed to enhance your hearing experience.
- Stay Informed: Continually update your knowledge about hearing health and available treatments.
- Be Proactive: Schedule regular audiology check-ups to monitor your condition.
Empower Your Hearing Journey Today
Understanding the complexities of hearing loss is the first step towards taking control of your auditory health. By familiarising yourself with the different types and causes of hearing loss, you can make empowered decisions about your hearing care. Whether you’re exploring hearing aids like the GN Resound Nexia microRIE 5 or seeking professional assistance for earwax removal, remember that you’re not alone in this journey. Embrace the benefits of audiology support and take charge of your hearing well-being today!